What is the difference between a screw conveyor and a spiral conveyor?
The terms "screw conveyor" and spiral conveyor refer to distinct types of conveying systems, differentiated by their design, mechanism, and application:
1. Screw Conveyor
Mechanism: Utilizes a rotating helical screw blade (flighting) within a trough or tube. The screw rotates to move bulk materials (e.g., powders, granules, sludge) along the conveyor's length.
Design:
Typically horizontal or inclined (up to ~20–30°).
Can be shafted (central shaft supporting the flighting) or shaftless (for sticky materials).
Materials are pushed through a sealed trough, preventing spillage.
Applications:
Agriculture (grain handling), wastewater treatment, food processing, and industrial bulk material transport.
Ideal for controlled feeding, mixing, or metering of materials.

2. Spiral Conveyor
Mechanism: Refers to a conveyor system arranged in a vertical or compact helical/spiral path, often using belts, rollers, or modular plastic chains. Gravity or mechanical drives move items along the spiral.
Design:
Compact vertical layout (e.g., ascending/descending helical paths).
Open design for unit loads (boxes, packages, products).
May include curved sections for space efficiency.
Applications:
Elevating or lowering items in packaging, bottling, or assembly lines.
Accumulation, cooling, or timing adjustment in industries like baking, logistics, or airports (baggage handling).
Summary
Screw conveyors are bulk material handlers using a rotating helical screw.
Spiral conveyors are space-efficient systems for elevating/lowering unit loads via a helical path, often using belts or rollers.
The confusion arises from overlapping terms, but their purposes and mechanisms are distinct.
How does a spiral elevator work?
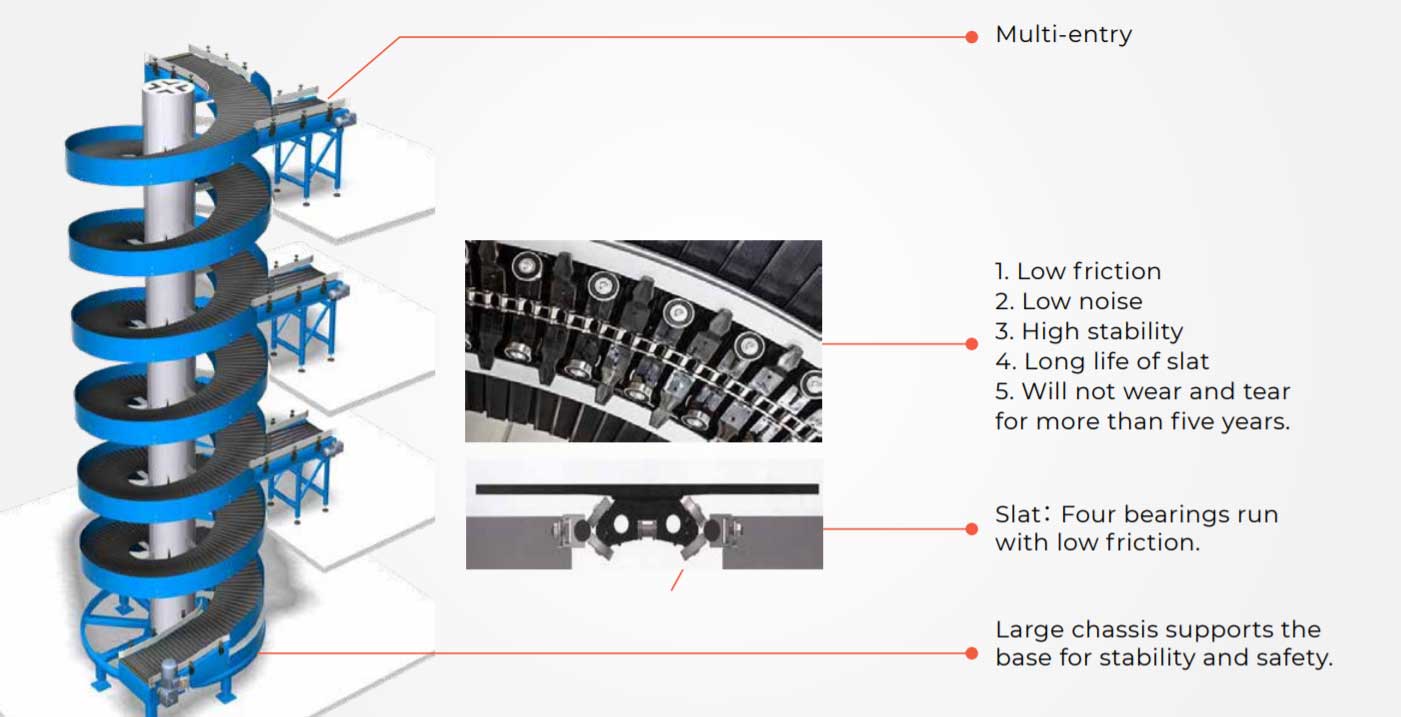
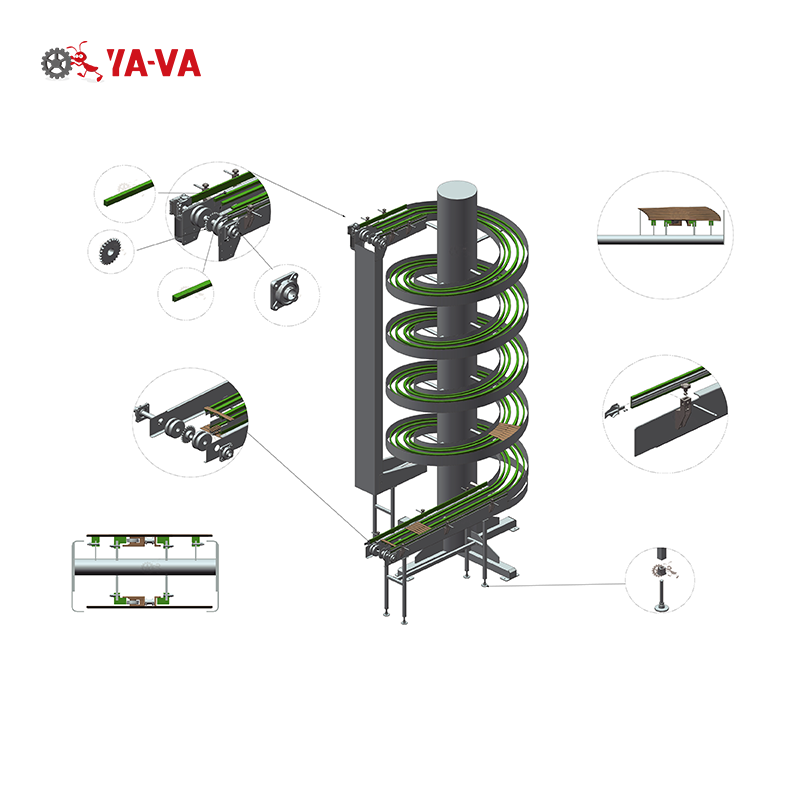
1. Basic Structure of a Spiral Conveyor
A spiral conveyor mainly consists of the following core components:
Spiral Track:
The helixshaped guide or slide, typically made of metal or highstrength plastic, used to direct the movement of materials or carriers.
Carrier:
Trays, chains, belts, or flexible components that carry materials, designed according to the characteristics of the materials.
Drive System:
The motor, reducer, and transmission device that provide power to drive the spiral track or carrier movement.
Support Frame:
The steel structure that supports the spiral track and drive system, ensuring the equipment operates stably.
Control System:
The electrical control system used to adjust speed, start and stop, and monitor the operating status of the equipment.

2. Working Principle of a Spiral Conveyor
The working principle of a spiral conveyor can be divided into two main types: fixed track and rotating track.
(1) Fixed Track Spiral Conveyor
Working Principle: The spiral track is stationary, and the carrier (such as a tray or chain) moves along the track, lifting materials from the bottom to the top.
Mode of Movement: The carrier ascends or descends along the spiral track through the drive system (such as a chain or belt).
Applicable Scenarios: Suitable for lightweight, regularly shaped materials (such as bottles, canned food).
(2) Rotating Track Spiral Conveyor
Working Principle: The spiral track itself rotates, and materials slide along the track by gravity or friction, lifting from the bottom to the top.
Mode of Movement: As the track rotates, materials ascend along the track under the combined action of centrifugal force and gravity.
Applicable Scenarios: Suitable for bulk materials or small parts (such as grains, particles, components).
3. Key Design Parameters of a Spiral Conveyor
Spiral Diameter:
Determines the equipment's footprint and transport capacity, usually designed according to material size and transport volume.
Pitch:
The vertical distance of the spiral track per turn, affecting the lifting speed of materials and equipment height.
Lift Height:
The total vertical transport height of the equipment, usually determined according to process requirements.
Conveying Speed:
The movement speed of materials or carriers, affecting the transport efficiency of the equipment.
Carrier Design:
The carrier is designed according to material characteristics (such as shape, weight, fragility) to ensure stable material transport.


4. Advantages of a Spiral Conveyor
Space Saving: The spiral design makes the equipment compact, suitable for factory layouts with limited space.
Efficient Vertical Transport: Can achieve continuous and efficient vertical transport, reducing material transfer time.
Adaptability: The track and carrier design can be customized according to material characteristics, suitable for various industries.
Low Maintenance: Simple structure, stable operation, and low maintenance costs.
5. Application Scenarios of a Spiral Conveyor
Food and Beverage Industry: Vertically lifting bottles, canned food to filling lines or packaging lines.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Transporting medicine bottles or packaging boxes to different workstations.
Warehousing and Logistics: Lifting and sorting goods in multistory warehouses.
Automotive Manufacturing: Transporting parts to different assembly stations.
6. Selection Recommendations in Industrial Design
Material Characteristics: Choose the appropriate carrier and track design according to the shape, weight, and fragility of the materials.
Space Limitations: Choose the spiral diameter and lift height according to the factory layout to optimize equipment footprint.
Process Requirements: Choose the appropriate drive system and control method according to transport speed and efficiency requirements.
Summary
The spiral conveyor achieves efficient vertical transport of materials through the coordinated action of the spiral track and carrier. Its compact design, efficient performance, and wide range of application scenarios make it one of the indispensable equipment in modern industrial production. Industrial engineers need to consider material characteristics, process requirements, and space limitations comprehensively when designing and using spiral conveyors to ensure the efficient and stable operation of the equipment.
Post time: Feb-25-2025



